Imagine opening an app on your phone and setting exactly how long you’d like to sleep, how much REM you need, and your exact wake up time. Your settings are then executed flawlessly, giving you exactly the sleep you need without the hassle of counting sheep.
It sounds like science fiction, but it’s far from it. Major entrepreneurs like Gabe Newell believe it will be one of the early applications when Brain Computer Interfaces (BCIs) become mainstream.
BCIs are a burgeoning new healthcare technology with massive potential. Companies like Elon Musk’s Neuralink, Gabe Newell’s Valve, and Synchron are making major headway in the field, which is inching toward mass market.
HOW DOES IT WORK?

BCIs essentially use software to decipher the chemical and electrical signals coming out of people’s brains and translate them into clicks or keystrokes on a computer or mobile device or even movement on a prosthetic arm.
Hans Berger discovered electrical activity in the human brain in 1924. This paved the way for Jacques Vidal to coin the term Brain Computer Interface in his 1973 paper “Toward Direct Brain-Computer Communications”. BCIs were first tested on monkeys in the 1970s while the first endeavors on human beings were performed in the 1990s.
The main thrust of today’s BCI research is dedicated toward building solutions which will help paralyzed people control assistive devices. Beyond healthcare, there are endless potential applications for BCIs. For example, BCIs could create significantly more immersive gaming experiences in which the gamer’s thoughts move the on-screen avatar.
HR companies could use BCIs to improve employee performance by sending an alert when they sense an employee’s attention levels are down or preventing them from operating heavy machinery when they are drowsy.
The medical community has a vested interest in seeing this technology develop. It could change the lives of generations of disabled people in the near future. As BCI start-up Paradromics put it: “The potential for BCI technology is only as impactful as how well it serves the immediate needs of patients with motor & communication impairments.”
The potential for #BCI technology is only as impactful as how well it serves the immediate needs of patients with motor & communication impairments
>>watch to the end>>#assistivetechnology #DDI #DirectDataInterface #braincomputerinterface #neurotech #neurotechrevolution pic.twitter.com/0UVXTpbm1i
— Paradromics Inc. (@paradromics) July 28, 2022
INVASIVE BCI VS. NON-INVASIVE BCI
There are essentially two types of BCIs: invasive and non-invasive.
Invasive BCIs involve a surgical implant of the device into the skull of the user. In ECOG (electrocorticography), an electrode plate is placed directly on the brain’s surface to measure its electrical activity. A second technique known as intracortical microelectrodes involves an implant that has two applications—stimulating and recording. Applications for stimulating incorporate sensory prosthetics—such as cochlear implants which provide the sensation of sound for the deaf.
Surgeries that require doctors to open up a patient’s skull are dicey to say the least. Non-invasive BCIs avoid this altogether. They can work using a variety of non-invasive technologies to measure brain activity, including EEG (electroencephalography), ERP (Event Related Potentials), MEG (Magnetoencephalography), fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resistance Imaging) or fNIRS (Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy).
ELON MUSK AND NEURALINK
Elon Musk founded Neuralink in 2016. Their goal was to create a device that would translate a person’s thoughts into actions. They have implanted chips into animals and notably released a video of a macaque monkey playing video games with its mind.
Although Neuralink is one of the major players of BCIs, they have lagged behind other companies in the field. Neuralink has yet to implant a BCI in humans. Their devices require highly invasive head implants which have drawn complaints from animal rights activists.
GABE NEWELL AND VALVE
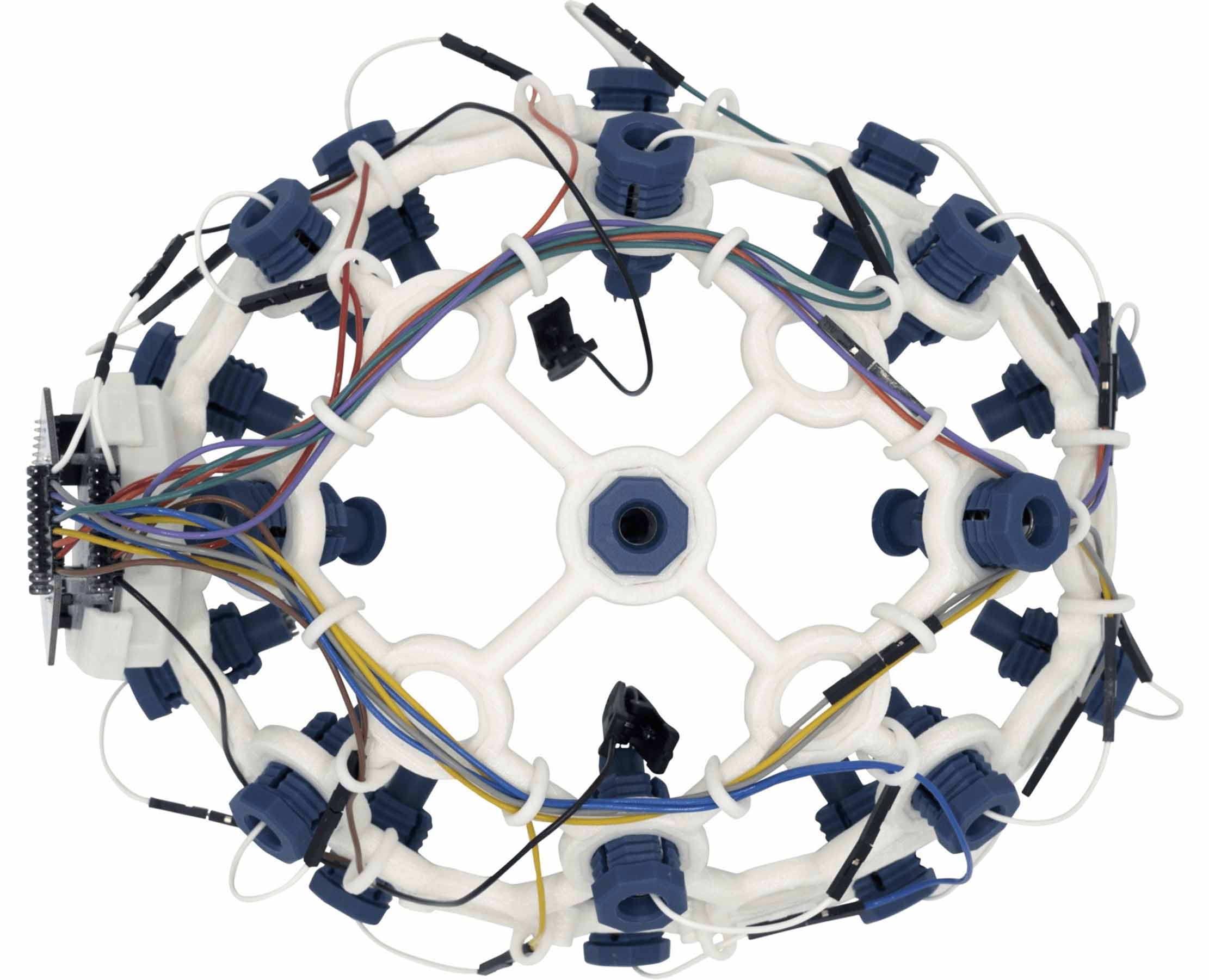
Another notable player in BCIs today is Gabe Newell, founder of the gaming company Valve. Valve’s goal is to use OpenBCI headsets to develop an open-source software platform that would make it easier for developers to understand the signals coming from people’s brains.
It could enable software to understand whether a player is enjoying a game and adjust the experience accordingly. He envisions a world where games can adjust their difficulty level depending on how the player is reacting mentally.
SYNCHRON TAKES THE CAKE
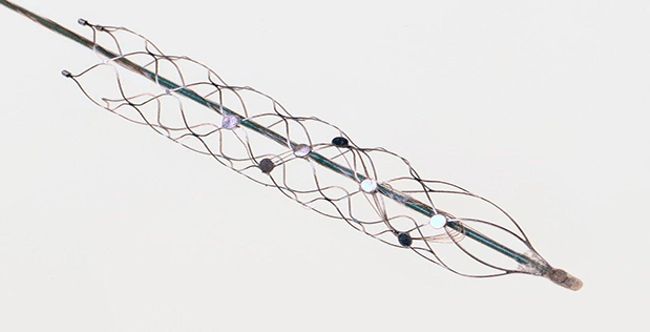
Synchron’s stentrode device is currently in the forefront of the market. Synchron beat Neuralink to the punch by securing FDA approval to implant its first device into a US patient. Synchron has an advantage because the stentrode can be inserted into the brain without cutting through a skull or damaging tissue. It’s a major innovation since it can be implanted safely minimizing risk for cerebral damage.
The stentrode is about the size of a AAA battery and can be planted endovascularly rather than through the brain. In fact, it’s so seamless, patients could be sent home the same day. Synchron has already implanted stentrodes into the brains of four patients in Australia suffering from neurodegenerative diseases. All of their patients have had no side-effects and have been able to send messages through WhatsApp as well as make online purchases using the device.
The stentrode is placed close enough to the brain to detect neural signals. Those signals, which could be a thought to move a body part or a cursor on a computer screen, are then relayed out to a computer using Bluetooth technology. In the words of Synchron CEO and founder Dr. Tom Oxley: “People who are paralyzed can still think about moving their body. It’s the muscles that don’t work… We essentially bypass the broken body by taking the information directly out of the brain to control devices that let them live independently.”
WHAT’S NEXT?
We can’t predict how quickly BCIs will become a consumer-facing technology, nor the bevy of applications they will enable. What we do know is that this field is growing and will in all likelihood become a game-changing technology that completely redefines life for the disabled, as well as how we interact with our devices.
Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn for more trending tech content!