Building applications for medical technology projects often requires extra attention from software developers. From adhering to security and privacy standards to learning new technologies and working with specialized file formats—developers coming in fresh must do a fair amount of due diligence to get acclimated in the space. Passing sensitive information between systems requires adherence to extra security measures—standards like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) are designed to protect the security of health information.
When dealing with medical images and data, one international standard rises above the rest: DICOM. There are hundreds of thousands of medical imaging devices in use—and DICOM has emerged as the most widely used healthcare messaging standards and file formats in the world. Billions of DICOM images are currently employed for clinical care.
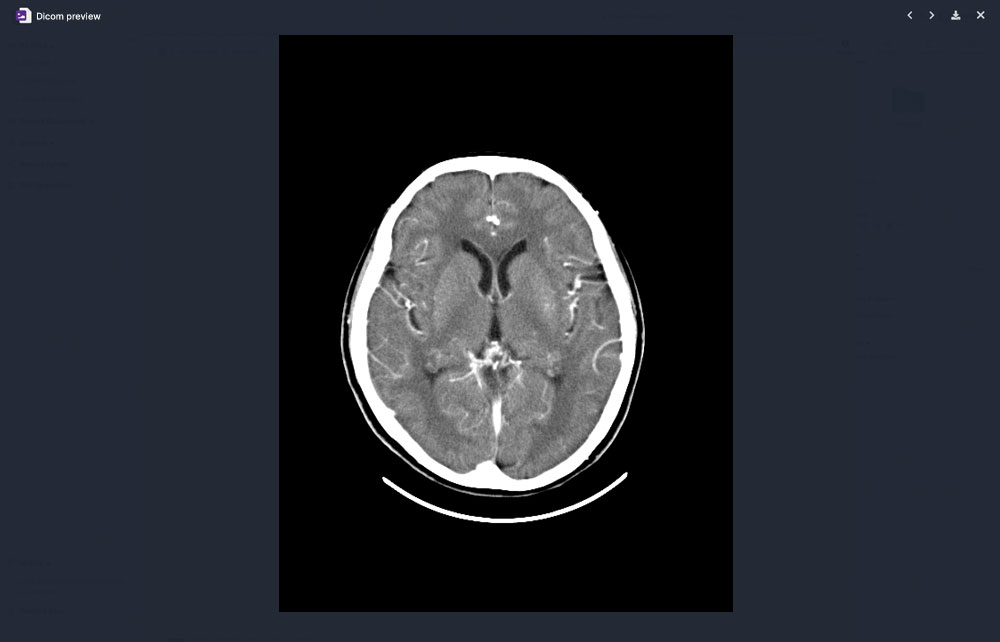
What is DICOM?
DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine. It’s the international file format and communications standard for medical images and related information, implemented in nearly every radiology, cardiology, imaging, and radiotherapy devices such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and more. It’s also finding increasing adoption in fields such as ophthalmology and dentistry.
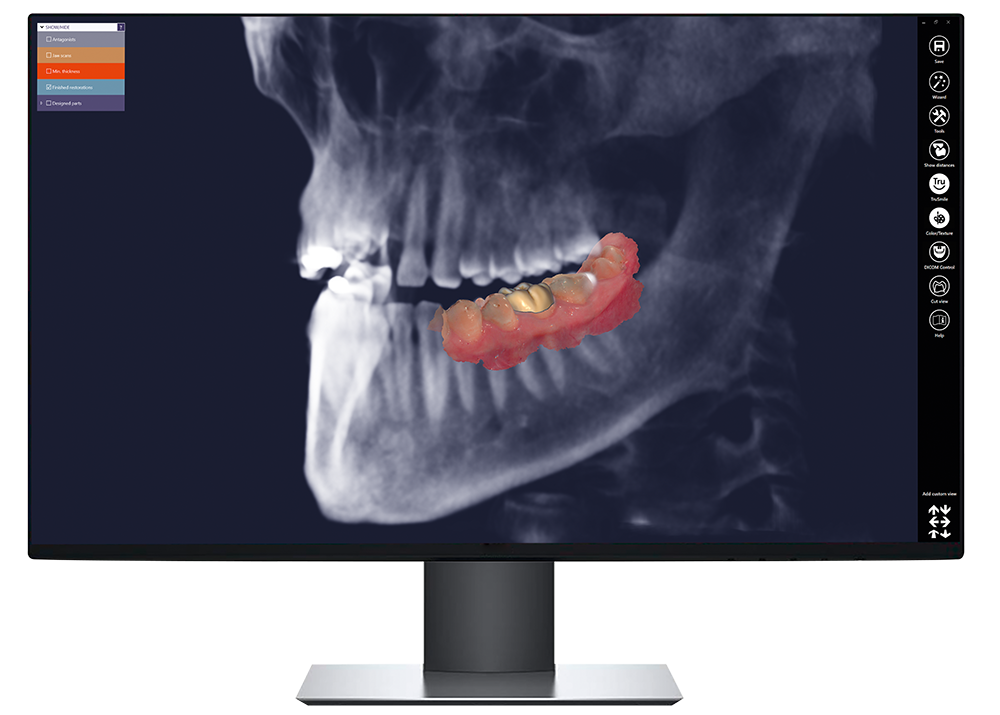
DICOM groups information into data sets. Similar to how JPEGs often include embedded tags to identify or describe the image, DICOM files include patient ID to ensure that the image retains the necessary identification and is never separated from it. The bulk of images are single frames, but the attribute can also contain multiple frames, allowing for storage of Cineloops.
The History of DICOM
DICOM was developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association (NEMA) in the 1980s. Technologies such as CT scans and other advanced imaging technologies made it evident that computing would play an increasingly major role in the future of clinical work. The ACR and NEMA sought a standard method for transferring images and associated information between devices from different vendors.
The first standard covering point-to-point image communication was created in 1985 and initially titled ACR-NEMA 300. A second version was subsequently released in 1988, finding increased adoption among vendors. The first large-scale deployment of ACR-NEMA 300 was in 1992 by the U.S. Army and Air Force. In 1993, the third iteration of the standard was released—and it was officially named DICOM. While the latest version of DICOM is still 3.0, it has received constant maintenance and updates since 1993.
Why Is DICOM Important?
DICOM enables the interoperability of systems used to manage workflows as well as produce, store, share, display, query, process, retrieve and print medical images. By conforming to a common standard, DICOM enables medical professionals to share data between thousands of different medical imaging devices across the world. Physicians use DICOM to access images and reports to diagnose and interpret information from any number of devices.
DICOM creates a universal format for physicians to access medical imaging files, enabling high-performance review whenever images are viewed. In addition, it ensures that patient and image-specific information is properly stored by employing an internal tag system.
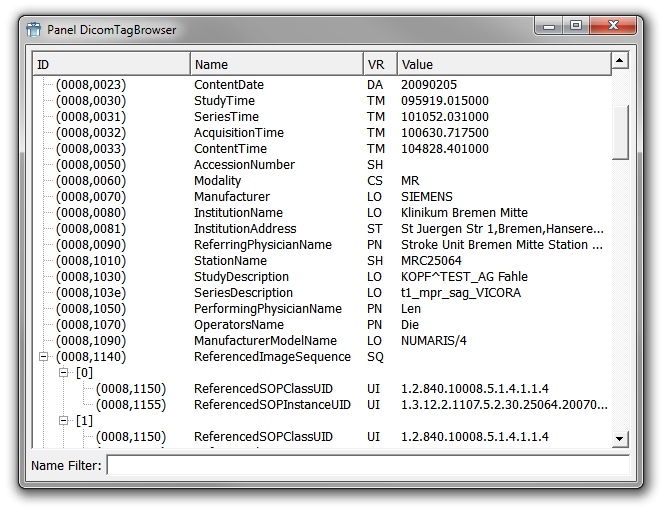
DICOM has few disadvantages. Some pathologists perceive the header tags to be a major flaw. Some tags are optional, while others are mandatory. The additional tags can lead to inconsistency or incorrect data. It also makes DICOM files 5% larger than their .tiff counterparts.
The Future
The future of DICOM remains bright. While no file format or communications standard is perfect, DICOM offers unparalleled cross-vendor interoperability. Any application developer working in the medical technology field would be wise to take the time to comprehensively understand it in order to optimize their projects.