In the previous installment of our blog series on indoor positioning, we explored all that Bluetooth 5.1 has to offer. This week, we will examine what may be a major wireless technology of the future: Ultra Wideband.
In September 2019, the inclusion of a U1 chip was listed among the innovations announced with the iPhone 11. The U1 chip provides Ultra Wideband (UWB) connectivity. Those knowledgable on UWB recognize that the inclusion of the U1 chip is a major step toward UWB becoming a household name technology like Bluetooth and WiFi.
HISTORY
UWB signifies a number of synonymous terms, including impulse, carrier-free, baseband, time domain, nonsinusoidal, orthogonal function and large-relative-bandwidth radio/radar signals.

UWB was first employed by Guglielmo Marconi in 1901 to transmit Morse code sequences across the Atlantic Ocean using spark gap radio transmitters. Development began in the late 1960s with pioneering contributions by Harmuth at Catholic University of America, Ross and Robbins at Sperry Rand Corporation, and Paul van Etten at USAF’s Rome Air Development Center in Russia. In the early 2000s, UWB was used in military radars, covert communication, and briefly in medical imaging applications such as remote heart monitoring systems. Its adoption lagged until commercial interests began exploring potential innovative uses.
MODERN USAGE
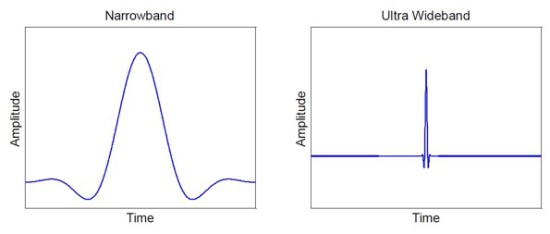
UWB is a short-range wireless communication protocol. It differs from WiFi and Bluetooth in that it uses radio waves operating at a very high frequency. Ultra Wideband alludes to the wide spectrum of GHz of the waves it utilizes, 5000 MHz or higher. Wi-Fi and LTE radio bands are about one-tenth as wide, typically ranging from 20 to 80 MHz. UWB is like a radar that can lock into objects to identify their location and transmit data.
Apple describes UWB technology as providing “spatial awareness”—it can continuously scan a room and precisely lock onto specific objects. One of the major applications for it in the iPhone 11 is the ability for the user to point their device at another device to target it for an Airdrop.
INDOOR POSITIONING
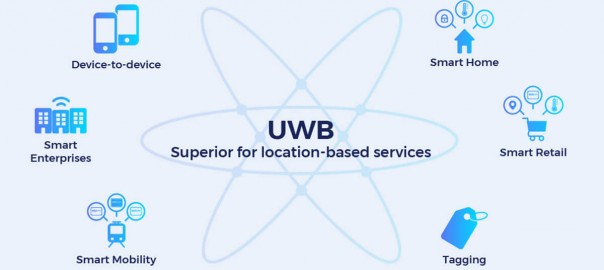
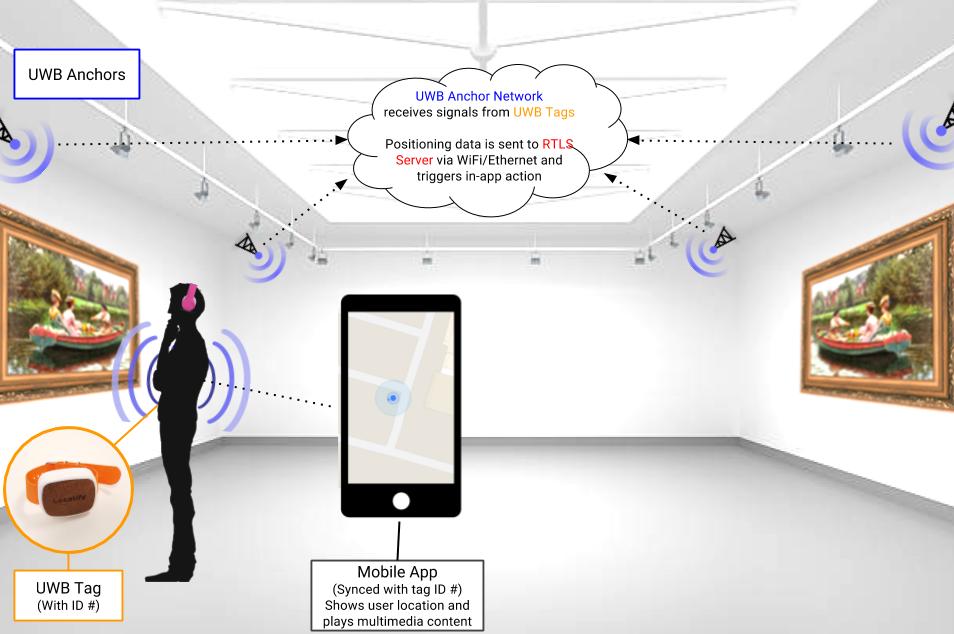
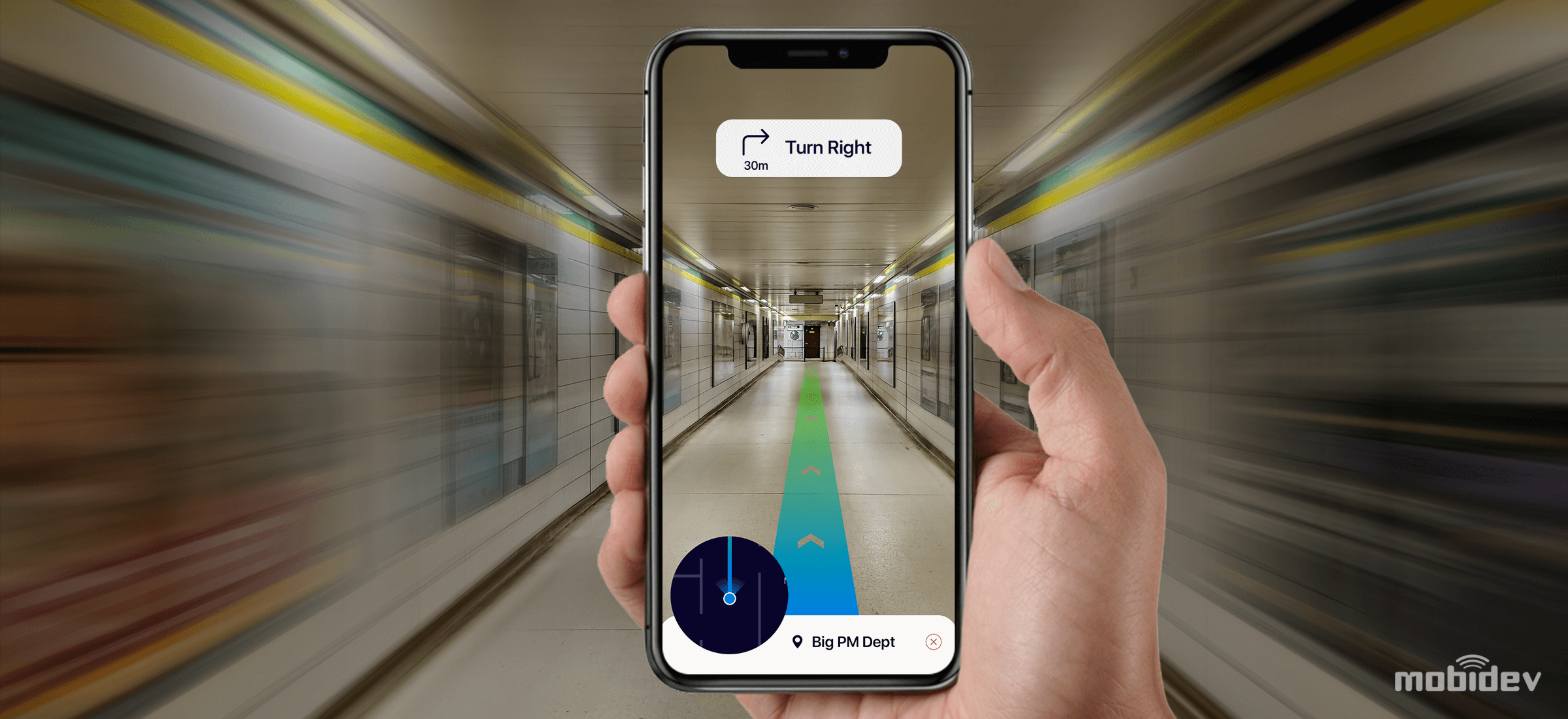
The primary usages of UWB are expected to be in indoor positioning, location discovery, and device ranging according to IDC research director Phil Solis. Compared to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, UWB is extremely low power and the high bandwidth makes it perfect for relaying mass amounts of data from a host device to other devices around 30 feet away. Unlike Wi-Fi, UWB is not particularly good at transmitting through walls, but its robustness against interference and high data rate (110 kbit/s – 6.8 Mbit/s) enable ideal, ultra-precise indoor positioning.
The inclusion of the UWB U1 chip in the iPhone 11 paves the way for applications in indoor mapping and navigation, smart home and vehicle access and control, enhanced augmented reality, and mobile payments that are more secure than NFC.
MASS ADOPTION
As new applications continue to emerge and the demand for indoor positioning increases, the major hurdle UWB faces is a lack of existing infrastructure. Apple and Huawei, the two largest smartphone makers in the world, are developing UWB projects, including chip and antenna production. Apple’s decision to include it in the iPhone 11 is the first time a UWB chip will be deployed on a smartphone. As trendsetters, it stands to reason that UWB will only grow in popularity from here and mass adoption may be inevitable.
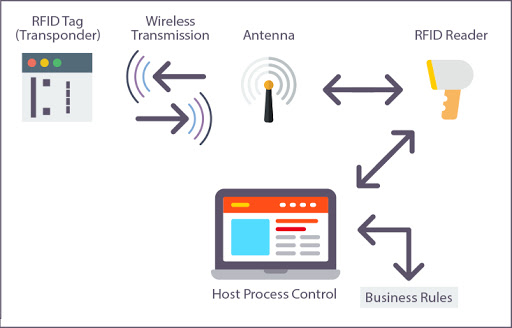
Stay tuned for the next entry in our Indoor Positioning blog series which will explore RFID Tags!