The world of professional sports has always been at the forefront of utilizing cutting-edge technologies to enhance the experience of fans and improve team performance. One of the most exciting emerging technologies in this space is augmented reality (AR), which has the potential to revolutionize the way sports are played and viewed. Augmented reality involves overlaying digital information and images onto the real world, in real-time, through a device like a smartphone or AR headset. In this blog post, we will explore the technical side of AR in professional sports, including examples of teams that are already using AR to gain a competitive edge on the field.
Player Training and Performance Analysis
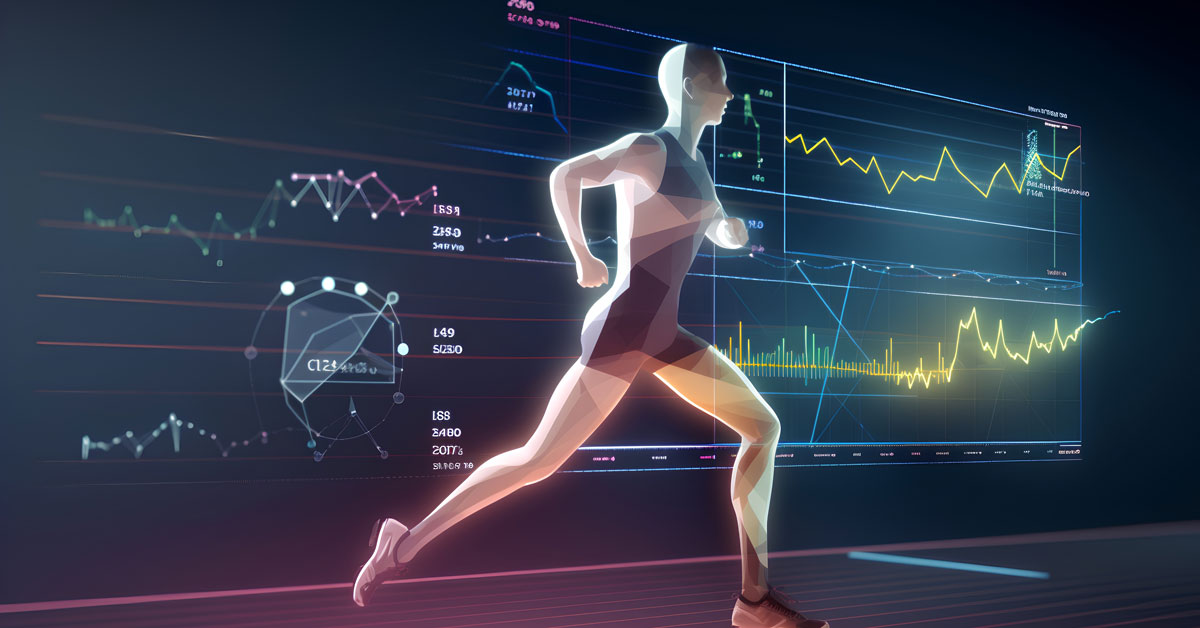

AR is already being used by professional sports teams to train and analyze player performance. For example, some basketball teams are using AR technology to track the shooting accuracy of their players during practice sessions. By overlaying digital targets and data onto a real basketball court, players can see how accurate their shots are and adjust their techniques accordingly. In football, AR is being used to simulate game scenarios and support off-field training for players. Coaches can use apps like NFL Game Theory to create plays and test them out in a digital environment. This allows players to become more familiar with different scenarios and improve their decision-making skills.
Enhancing Fan Engagement and Experience
In terms of fan engagement and experience, AR has opened up exciting new possibilities for professional sports teams. Manchester City FC, for instance, launched an AR app called “CityVR” in 2019 that allowed fans to explore their Etihad Stadium in 360 degrees, access exclusive content, and engage with the team in a fresh, immersive way. Similarly, the NBA’s Golden State Warriors used AR to improve fan engagement by bringing fans closer to the team’s pre-game rituals and player interactions through an official mobile app.
Several NFL teams, like the Tampa Bay Buccaneers and Baltimore Ravens, have also harnessed the power of AR to bring team mascots or famous players into fans’ surroundings through their mobile apps. Meanwhile, FC Barcelona enabled fans to interact with live AR stats, player statistics, and take a virtual tour of the iconic Camp Nou Stadium via their “Barça Live” AR app.
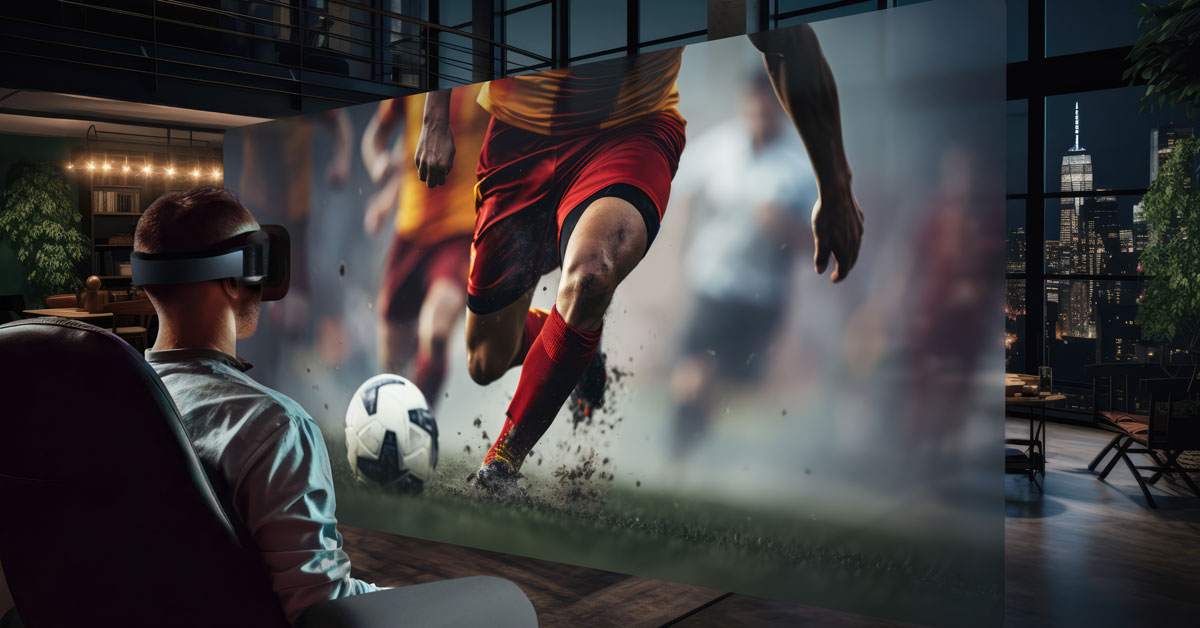

The Los Angeles Dodgers took the AR experience to the next level by providing AR glasses to fans during their games, overlaying real-time player statistics and information onto their view of the field. The San Francisco 49ers have also utilized AR in player training, developing a VR/AR-based program called “VRtize” to enhance game scenario understanding and decision-making among players.
The New York Yankees used AR to create interactive experiences for fans such as virtual tours of Yankee Stadium, while Formula 1 infused the fan experience with AR, enabling access to live data, track positions, and driver information during races via their F1 AR app. Various NHL and MLB teams have similarly leveraged AR to engage fans with initiatives like the Minnesota Wild’s AR app for photos with virtual players and the Boston Red Sox’s AR-based scavenger hunt within Fenway Park.
These diverse examples demonstrate how professional sports teams are leveraging augmented reality to connect with fans, enhance player performance, and create unique, interactive experiences both inside and outside the stadium. As AR technology continues to evolve, it is slated to play a significant role in shaping the future of sports entertainment.
Virtual Advertising

AR also provides a new way for teams to monetize their advertising real estate. Virtual advertising involves overlaying digital advertisements onto the real-world environment. This has the potential to revolutionize the way teams approach sponsorship deals, as they can now sell virtual ad space rather than relying solely on traditional advertising methods. For example, during an NFL game, virtual advertisements could be overlaid onto the field, visible to TV viewers but not to fans in the stadium.
AR-Enhanced Stadiums
Looking to the future, we can expect to see more stadiums and arenas incorporate AR technology directly into their architecture. For example, the forthcoming home stadium for the Golden State Warriors will include AR screens in its luxury suites, giving fans a more immersive experience during games. The Australian National Rugby League is also preparing to rollout AR technology in its stadiums, with the goal of enhancing the viewing experience for fans.

Challenges and Limitations
While AR has the potential to revolutionize professional sports, there are still challenges and limitations that must be overcome. One of the biggest issues is the cost and complexity of implementing AR technology. It requires significant investment in both hardware and software, as well as the expertise to develop and maintain AR applications. There are also concerns around data privacy and security, as AR applications often collect sensitive personal information.
In conclusion, augmented reality has the potential to significantly impact the world of professional sports, providing players with new training and analysis tools, fans with a more immersive viewing experience, and teams with new sources of revenue. However, there are still challenges and limitations that need to be overcome before AR becomes mainstream in this space. The good news is that we are already seeing some examples of teams successfully implementing AR, and as the technology becomes more advanced and accessible, we can expect to see even more exciting applications emerging. As always, staying ahead of the curve and embracing new technologies will be critical for maintaining a competitive edge in professional sports.