On October 23rd, four brand new iPhone 12 models were released to retailers. As the manufacturer of the most popular smartphone model in the world, whenever Apple delivers a new device its front-page news. Mobile app developers looking to capitalize on new devices must stay abreast of the latest technologies, how they empower applications, and what they signal about where the future of app development is headed.
With that in mind, here is everything app developers need to know about the latest iPhone models.
BIG DEVELOPMENTS FOR AUGMENTED REALITY
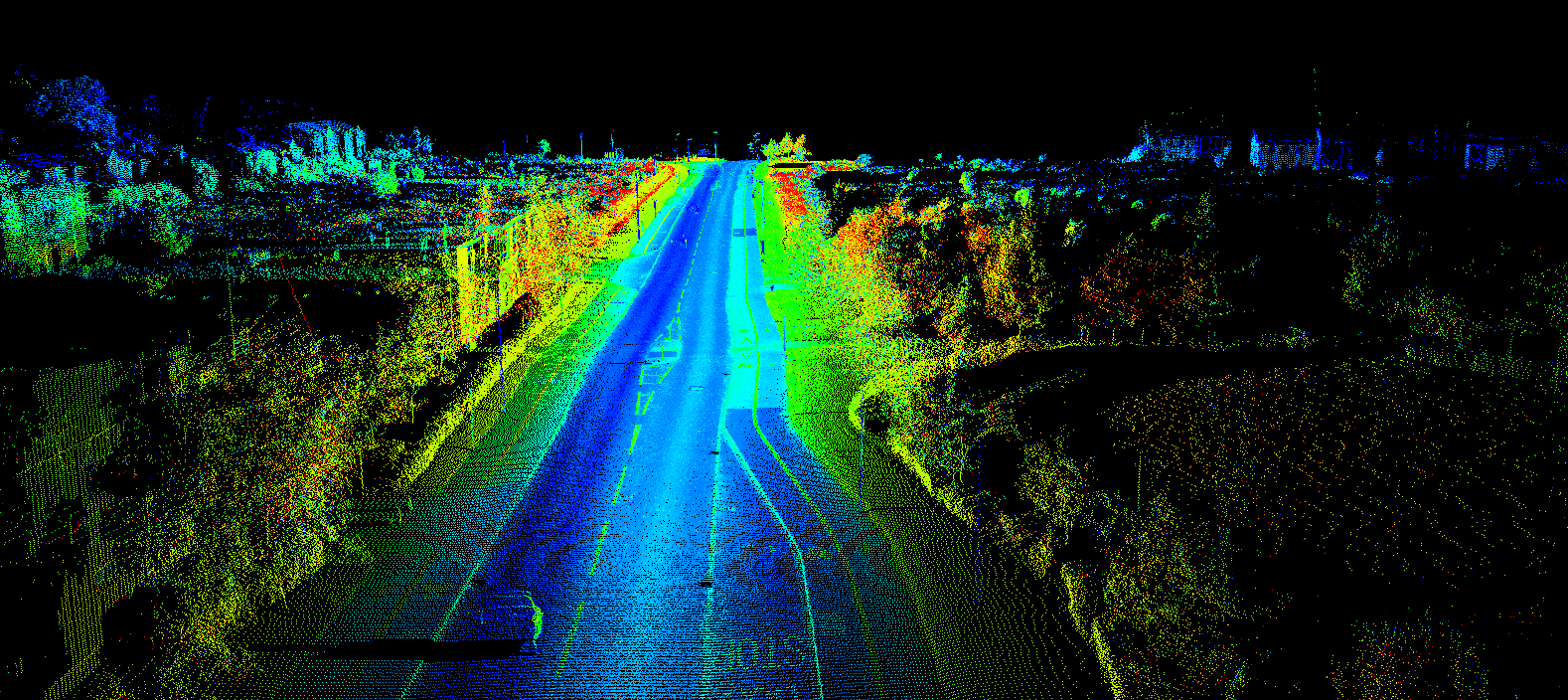

On a camera level, the iPhone 12 includes significant advancements. It is the first phone to record and edit Dolby Vision with HDR. What’s more, Apple has enhanced the iPhone’s LiDAR sensor capabilities with a third telephoto lens.
The opportunities for app developers are significant. For AR developers, this is a breakthrough—enhanced LiDAR on the iPhone 12 means a broad market will have access to enhanced depth perception, enabling smoother AR object placement. The LIDAR sensor produces a 6x increase in autofocus speed in low light settings.
The potential use cases are vast. An enterprise-level application could leverage the enhanced camera to show the inner workings of a complex machine and provide solutions. Dimly lit rooms can now house AR objects, such as Christmas decorations. The iPhone 12 provides a platform for AR developers to count on a growing market of app users to do much more with less light, and scan rooms with more detail.
The iPhone 12’s enhanced LiDAR Scanner will enable iOS app developers to employ Apple’s ARKit 4 to attain enhanced depth information through a brand-new Depth API. ARKit 4 also introduces location anchors, which enable developers to place AR experiences at a specific point in the world in their iPhone and iPad apps.
With iPhone 12, Apple sends a clear message to app developers: AR is on the rise.
ALL IPHONE 12 MODELS SUPPORT 5G
The entire iPhone 12 family of devices supports 5G with both sub-6GHz and mmWave networks. When iPhone 12 devices leverage 5G with the Apple A14 bionic chip, it enables them to integrate with IoT devices, and perform on ML algorithms at a much higher level.
5G poses an endless array of possibilities for app developers—from enhanced UX, more accurate GPS, improved video apps, and more. 5G will reduce dependency on hardware as app data is stored in the cloud with faster transfer speeds. In addition, it will enable even more potential innovation for AR applications.
5G represents a new frontier for app developers, IoT, and much more. Major carriers have been rolling out 5G networks over the past few years, but access points remain primarily in major cities. Regardless, 5G will gradually become the norm over the course of the next few years and this will expand the playing field for app developers.
WHAT DOES IT MEAN?
Beyond the bells and whistles, the iPhone 12 sends a very clear message about what app developers can anticipate will have the biggest impact on the future of app development: AR and 5G. Applications employing these technologies will have massive potential to evolve as the iPhone 12 and its successors become the norm and older devices are phased out.