In the previous installment of our blog series on indoor positioning, we explored the future of Ultra Wideband technology. This week, we will examine RFID Tags.
The earliest applications of RFID tags date back to World War II when they were used to identify nearby planes as friends or foes. Since then, RFID technology has evolved to become one of the most cost-effective and easy to maintenance indoor positioning technologies on the market.
WHAT IS RFID?
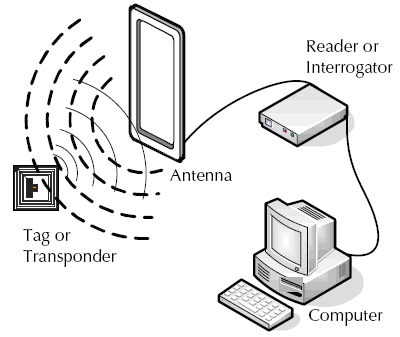
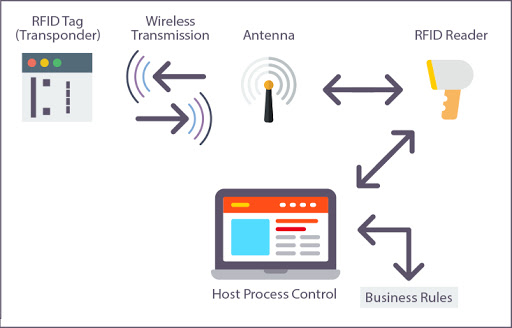
RFID refers to a wireless system with two components: tags and readers. The reader is a device with one or more antennae emitting radio waves and receiving signals back from the RFID tag.
RFID tags are attached to assets like product inventory. RFID Readers enable users to automatically track and identify inventory and assets without a direct line of sight with a read range between a few centimeters and over 20 meters. They can contain a wide range of information, from merely a serial number to several pages of data. Readers can be mobile and carried by hand, mounted or embedded into the architecture of a room.
RFID tags use radio waves to communicate with nearby readers and can be passive or active. Passive tags are powered by the reader, do not require a battery, and have a read range of Near Contact – 25 Meters. Active tags require batteries and have an increased read range of 30 – 100+ Meters.
WHAT DOES RFID DO?
RFID is one of the most cost-effective and efficient location technologies. RFID chips are incredibly small—they can be placed underneath the skin without much discomfort to the host. For this reason, RFID tags are commonly used for pet identification.
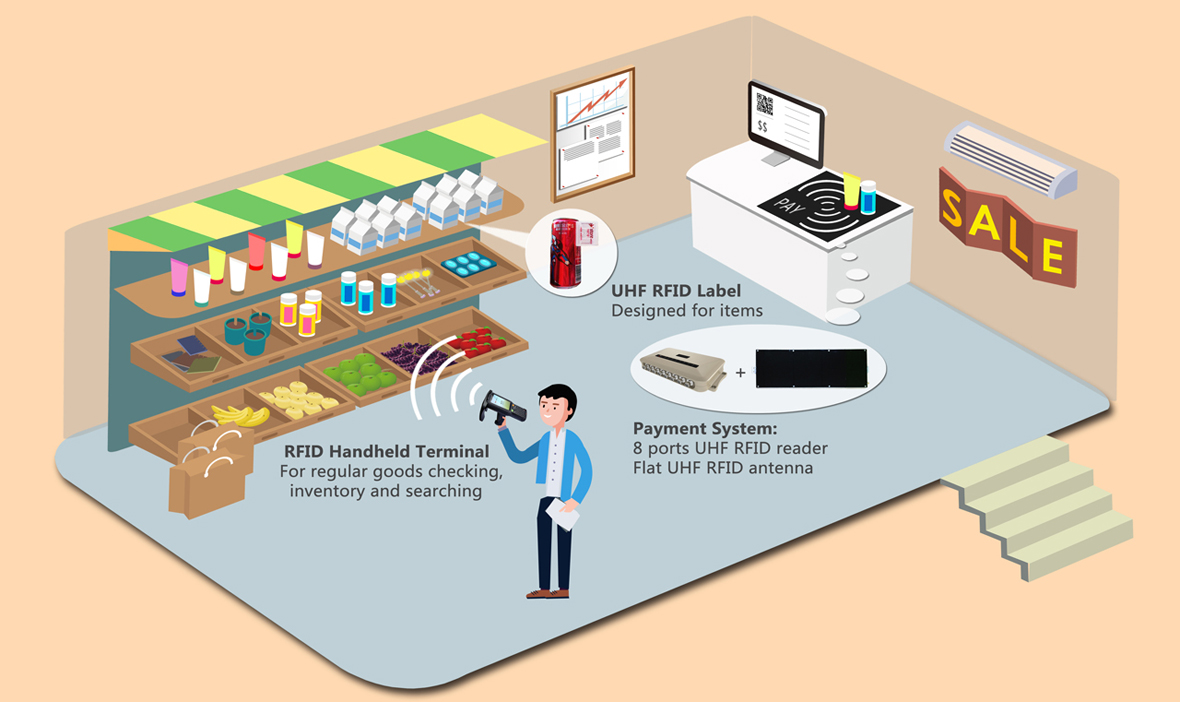
One of the most widespread uses of RFID is in inventory management. When a unique tag is placed on each product, RFID tags offer instant updates on the total number of items within a warehouse or shop. In addition, it can offer a full database of information updated in real time.
RFID has also found several use cases in indoor positioning. For example, it can identify patients and medical equipment in hospitals using several readers spaced out in the building. The readers each identify their relative position to the tag to determine its location within the building. Supermarkets similarly use RFID to track products, shopping carts, and more.
RFID has found a wide variety of use cases, including:
- Race timing
- Supply chain management
- Inventory/asset tracking
- Tolling
- Jewel tracking
- Real-Time Location Systems
WHAT ARE THE CONS OF USING RFID?
Perhaps the biggest obstacle facing businesses looking to adopt RFID for inventory tracking is pricing. RFID tags are significantly more expensive than bar codes, which can store some of the same data and offer similar functionality. At about $0.09, passive RFID tags are less expensive than active RFID tags, which can run from $25-$50. The cost of active RFID tags causes many businesses to only use them for high-inventory items.
RFID tags are also vulnerable to viruses, as is any technology that creates a broadcast signal. Encrypted data can help provide an extra level of security; however, security concerns still often prevents larger enterprises from utilizing them on the most high-end merchandise.
OVERALL
RFID tags are one of the elite technologies for offering inventory management with indoor positioning. Although UWB and Bluetooth BLE beacons offer more precise and battery-efficient location services, RFID is evolving to become more energy and cost efficient.
Stay tuned for the next entry in our Indoor Positioning blog series which will explore AR applications in indoor positioning!